Fossil Groundwater Lake Unearthed Beneath Sicilian Mountains: 6 Million Years

Millions of years ago, freshwater seeped into the Earth’s crust and was trapped beneath the Sicilian Mountains in Sicily, generating an aquifer that has remained unchanged for thousands of feet below the surface.
Approximately 6 million years ago, freshwater seeped into the Earth’s crust and got confined beneath the Hyblaean Mountains in Sicily, creating an aquifer that has remained stationary ever since.
The researchers are optimistic that extracting the freshwater may mitigate the water shortage problem in Sicily. Furthermore, they anticipate that this discovery will catalyse conducting similar investigations into deep groundwater reserves in other regions of the Mediterranean.
How To Protect Your Privacy On The Internet From Malicious Websites: 8 Ways
Sicilian Mountains
The Sicilian Mountains are arranged within the southeastern locale of Sicily, bounded by Ragusa, Syracuse, and Catania, and it may be level.
The tallest crest, Mount Lauro, found on the boundary between Ragusa and Syracuse, is around 987 meters above ocean level. The appearance of the level has been significantly formed, at times within the shape of wanders, by the courses of a few waterways and downpours.
The parallels between the Hyblaean clefts and canyons in North America lead most to classify them as canyons. But within the nearby language, they are called the Hyblaean “caves,” with Cavagrande del Cassibile hailed as the “foremost wonderful canyon of the whole Hyblaean level” and the foremost gone by.
The old occupants of these mountains cleared out behind necropolises, catacombs, and shake churches that have remained intaglio for millennia.
CERN: The Organization for European Research on Nuclear
Aqueous Fossils


Ancient, undisturbed water, frequently found in aquifers or other underground arrangements, is known as fossil or paleowater. Subglacial lakes like Lake Vostok in Antarctica and water from long-gone universes illustrate fossil water.
It is expected to analyse isotopically following an arrangement to decide the period since the water was attacked. Choosing the “fossil” status of water—whether or not that water has been displaying in that zone for a long time—requires calculating the aquifers’ stream, energise, and misfortunes, which can present a part of equivocalness.
Some aquifers lay underneath expansive swaths of land and are hundreds of meters deep. Both the logical information base and investigative strategies in this zone are expanding at a rapid pace. The age and behaviour of the water inside numerous aquifers have not been well considered or are the subject of debate.
Remarkable Fossil Water Sources
Aquifer of Ogallala
The Ogallala or Tall Fields Aquifer is found underneath 450,000 square km of eight US states. It is among the world’s most broad freshwater reserves. Alluvial stores that have yet to be compacted make up the aquifer.
Analysts have decided that the groundwater in this aquifer was stored amid the damp period promptly after the final glacial maximum. Precipitation cannot enter the aquifer for a noteworthy parcel of its surface region due to an impervious calcrete layer. Very minor recharge rates have been recognised in other parts of the aquifer.
A parcel of individuals live over the aquifer, and a parcel of ranches depend on it for water. Overwhelming extraction has caused the water table to drop drastically in a few districts. Instead of levelling off, exhaustion rates have been climbing over the past few decades.
System of the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer
Approximately 2,000,000 square km of the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer Framework lies underneath the surface of Sudan, Libya, Egypt, and Chad in northeastern Africa.
The lion’s share of its structure is made up of numerous sandstone aquifers that are connected powerfully. Parts of the framework are thought to be contained but marginally cracked because of impermeable strata like marine shales. The precise age of the water’s testimony ranges from four thousand to twenty thousand years.
The tenants of the region over the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer Framework have long put a premium on the water that flows through it. Maintaining a strategic distance from quick exhaustion and worldwide fighting within the modern period would require fastidious cross-border checking and arranging due to rising requests.
Egypt and Libya are planning advancement initiatives to tap into the fossil water within the aquifer.
Discovery of a ‘Vanishing’ Galaxy From the Big Bang Revealed by the James Webb Space Telescope
Groundwater Sources Within the Kalahari Desert
Central southern Africa, including South Africa, Namibia, and Botswana, are home to the Kalahari Leave. The area’s geography has striking karst formations. To renew the aquifers below, the more significant part of precipitation within the zone recently dissipated. It has a chance to do so.
There has been much discussion and thinking about whether or not the aquifers within the range get considerably revived. According to isotopic fingerprints found in cave sandstone, a profound within the Kalahari’s northern segment is a flat aquifer fixed off for ages.
‘Fossil Groundwater Lake’ Uncovered Underneath Sicilian Mountains; Age: 6 Million Years.
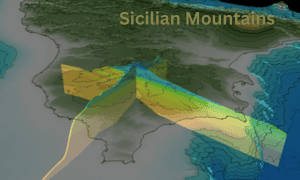

Aquifers shaped hundreds of feet underneath Sicily’s Hyblaean Mountains from new water that leaked into the Earth’s hull six million years back have remained unaltered ever since.
Fresh proof proposes that sizable water retained into the Earth’s outside six million years prior may still lurk beneath a Sicilian mountain run, concurring with later studies.
When the Mediterranean Ocean dried up due to the rising sea foot encompassing the Strait of Gibraltar, the new water likely got caught underneath amid the Messinian saltiness emergency.
Analysts found that this event likely empowered rainfall to leak into the Earth’s hull after uncovering the seafloor to it (Communications Earth & Environment, 22 November).
An aquifer, filled with precipitation, has been consistently rising underneath the Hyblean Mountains in southern Sicily, Italy, for a bit of time presently, and its profundity ranges from 700 to 2,500 meters.
Using freely available data from these wells, researchers within the current ponder examined profound groundwater saves in and around the Gela arrangement. This arrangement is known to be an oil supply and includes numerous deep wells.
More water could be stored within the aquifer than in Scotland’s Loch Ness, concurring with the 3D models they created. The assessed volume of water could be 4.2 cubic miles (17.5 cubic kilometres).
Using the 3D models, the analysts could remember the topographical history of the considered locale, which included the central Mediterranean’s Hyblaean and Malta Levels.
Agreeing to their discoveries, new water leaked into Earth’s hull to a profundity of a few thousand feet underneath present-day ocean levels due to the saltiness emergency amid the Messinian period (7.2 million to 5.3 million a long time ago).
Due to the emergency, parts of the Mediterranean had an ocean level decrease of around 7,870 feet (2,400 meters).
According to Lorenzo Lipparini, a geoscientist from the College of Malta,
Roma Tre University, and Italy’s National Organization of Geophysics and Volcanology, the “fossil groundwater pool” in the long run filled a layer of carbonate rocks that capacities like “a sort of wipe,” with liquids contained inside the spaces between the shake particles. Lipparini spoke to Live Science via email.
However, for this theory to be valid, Lipparini and his colleagues had to discover a way to transfer precipitation (rain and snow) from the Mediterranean seafloor to the subterranean Gela formation.
A submerged cliff that stretches southward from the eastern edge of Sicily, the Malta Escarpment, which is 190 miles (300 kilometres) long, “could be a candidate for such a direct connection,” according to the academics who published the report. Put differently, the pipe that has gone missing is probably located inside the escarpment.
The almost 700,000-year-long Messinian salinity crisis came to a sudden conclusion due to an “extremely rapid” increase in sea levels, which may have altered pressure conditions and “deactivated the complete noted the study’s authors.
The researchers also thought that during the salinity crisis, sediments and mineral deposits might have blocked the conduit along the Malta Escarpment, such that salt water and fresh water couldn’t interact within the formation for millions of years.
The group is crossing its fingers that their finding will encourage more in-depth groundwater investigations across the Mediterranean, which may bring fresh water up to assist Sicily’s water shortage.
Hydrology of Groundwater


Water that’s found below the Earth’s surface, within the hole between soil particles or rock layers, is known as groundwater. To distinguish it from surface water—found in enormous bodies like lakes or oceans or streaming overland in streams—it is regularly alluded to as subsurface water.
The hydrologic cycle, which is the progressing development of water within the Earth-atmosphere framework, has associations with both surface and underground water.
Water Stream in Aquifers
The hydrology term for a shake arrangement that both stores and discharges water in critical amounts is an aquifer. On the off chance that the water-filled pore spaces within the shake can be fixed, water can stream through the rock’s framework.
Aquifers are sometimes known as water focal points, zones, or strata. A major source of new water on Earth is the capacity to burrow wells into different aquifers.
Categories
A confined aquifer could be a water-bearing shake that’s either firmly stuffed or secured by an impermeable shake arrangement that prevents water from entering the layer underneath.
In spite of the fact that the limiting strata or layers don’t effectively pass on water, they steadily spill an impressive quantity of water to supplement generation from most aquifers; thus, there are likely exceptionally few restricted aquifers.
Fill-up
Aquifers get more water when water gradually leaks back into the ground through waste. The method of this runoff is called groundwater revive. When precipitation inputs to soil outperform evapotranspiration misfortunes, groundwater energise rates are at their most elevated.
Water that’s exceptionally profound down may be exceptionally old, perhaps as a result of a different climate administration that was in place long prior. The water from the Nubian Sandstone Aquifer Framework is a prime case; it extends over numerous countries in what is presently the Sahara.
Water systems and water supply are two major clients of the water. This water is thousands of a long time ancient, according to radioisotope dating.
And fair as the gigantic Ogallala Aquifer within the American Incredible Fields halted accepting revived water from the Rough Mountains when it was created within the Pliocene Age (5.3–2.6 million years back), so as well does it presently.
The practice of extricating and utilising groundwater, which climate administration isn’t recharging, is called groundwater mining.
Mineral Spring Water


Mineral water is characterised as water with a tall concentration of dissolved gasses or minerals. Calcium carbonate, magnesium sulfate, potassium, and sodium sulfate are minerals found in mineral water that begin from normal springs. Gasses like carbon dioxide or hydrogen sulfide can also be impregnated into it.
Salts or carbon dioxide can be included to refined water to make mineral water in a lab. Characteristic and engineered mineral waters contrast considerably in mineral concentration, with the previous now and then having lower levels than standard tap water.
Precipitation
All of the water vapour and strong particles that drop from the sky and arrive on the Soil is called precipitation. Sprinkle, precipitation, snow, snowflakes, ice, and accost all drop inside this category of particles. A fast outline of precipitation is given in this article.
Particles in precipitation vary essentially in estimate from those in clouds. The mass of one raindrop is approximately break even with that of one million cloud beads. Particles of precipitation are able to create it from the cloud to the ground at tall rates due to their enormous size.
Hydrology of the Vadose Zone
The vadose zone alludes to the area where discussion may circulate over ground level. Depending on the silt molecule estimate, the capillary periphery over the water table can be found in this zone as well. All through coarse-grained settings.
The periphery on coarser-grained materials tends to be complementary and more slender toward the best, whereas that on finer-grained materials can be more articulated and uneven. The thickness of the vadose zone can extend from zero to hundreds of feet, depending on a number of circumstances.
The sort of soil fabric and the encompassing environment are two of these variables. Vadose water, also known as gravitational water, is the water in this space that’s falling due to the constrain of gravity.
Hydrology of the Water Table
The term “water table” alludes to the highest layer of the subsurface, where water is always leaking into the soil or rocks. Underneath the water table is the groundwater zone, and over it is the capillary periphery, also known as the zone of air circulation.
Due to climate contrasts and the amount of precipitation plants utilise, the water table encounters regular and yearly changes. Taking out as well as much water from wells or misleadingly filling them up too has an impact.
Artesian Well:


An artesian well does not require pumping but instead allows water to flow naturally under pressure. When a layer of porous rock, like sandstone, dips slightly and collects water along its surface at a level above the ground at the location of the well, the hole is excavated.
At the outcrop, water seeps into the aquifer (the layer of rock that contains water) but can’t escape because of the impermeable rock layers (like shale) on either side.
Water is drawn to the surface of an aquifer-drilled well by the weight of the water, which is known as hydrostatic pressure. The pressure for the continuous flow is sustained by the water’s continued penetration into the aquifer at the intake area.
Cryoseism Seismology
A phenomenon known as cryoseism occurs when water in saturated ground freezes rapidly, causing soil or rock to fracture suddenly. Because they create ground shaking, jolts, booms, and vibrations, these seismic occurrences are occasionally confused for actual earthquakes.
As glaciers make their way to the ocean, they may cause cryoseisms in mountainous and polar areas by lurching forward and after or skidding over a rocky substrate.
Are you searching for new discoveries, information and articles? Then you are in the right place. Click on blogkingworld.com for more highly informative and helpful articles, sign up for our newsletter for free, follow me on LinkedIn, and please like and share it with your friends and family. Also, comment for our further guidance; thanks for your precious time.




